Resources
The Research Department has put together some useful information to help aspiring researchers navigate the complex research journey.
- Types of research
- Funding—non-commercial funding/commercial funding
- National Institute for Health and Research (NIHR)
- NIHR support for nursing, midwifery and allied health professionals (NMAHPs)
- Setting up a project
- Health Research Authority (HRA)
- Sponsorship
- Education and Training
- Tissue Bank
Types of research
There are different types of research involving human participation, including clinical trials, behavioural research and translational research.
Clinical trials
Clinical trials aim to establish new knowledge about specific products in disease prevention, detection, diagnosis and treatment. The item investigated could be a Drug, a Food product or a Medical device.
Clinical Trials of Investigational Medicinal Products (CTIMPs)
CTIMPs are defined as any investigation of a drug or food product in human subjects intended to:
- discover or verify the clinical, pharmacological and/or other pharmaco-dynamic effects of an investigational product(s),
- to identify any Adverse Reactions (ARs) to an investigational product(s),
- to study absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of one or more such products with the object of ascertaining its safety or efficacy.
CTIMPs follow strict regulatory and governance laws as defined by The Medicines for Human Use (Clinical Trials) Regulations 2004 (SI 2004 No. 1031, amended 2006), and require authorisation from the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency.
Medical devices
Medical devices include any healthcare product intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent disease and does not primarily work by effecting a chemical change in the body, like biologic and pharmaceutical drugs do.
Examples for medical devices include catheters, crutches, diagnostic test kits, electrodes, intraocular lenses and pacemakers.
Clinical investigations aimed at demonstrating the safety and performance of medical devices that do not yet meet the relevant regulatory compliance (non-CE marked), or established medical devices (= CE marked) that have been modified or are to be used for a new purpose may be regulated under the Medical Devices Regulations 2002 and require approval from the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency.
Behavioural research
Behavioural research tries to understand the risk factors to developing a disease in terms of people’s individual characteristics, lifestyles and emotional and social circumstances, and promote treatments aimed at preventing or changing risky behaviours.
Good examples of behavioural studies include:
- Lifestyle interviews and/or questionnaires about eating, drinking, smoking, exercise and communication habits and coping strategies
- Behaviour programs aimed at positively changing lifestyle habits, such as exercise classes, healthy eating sessions and counselling.
Translational research
Translational research – also known as ‘bench to bedside’ research – involves applying basic research results into practice for example by creating new treatment and diagnostic tools based on the results.
Hospitals and health care professionals work closely with researchers and feedback on treatment efficacy which helps focus research into the most useful areas. A good example of this is cancer research where cooperation between clinicians, researchers and pharmaceutical companies has helped generate several new chemical compounds that are better at treating and targeting specific aspects of cancer with less harmful effects. This is known as ‘bedside to bench’ research.
Non-commercial funding
UK Research and Innovation
UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) invest approximately £2.8 billion per annum in a wide range of research, including medical, biological and social sciences. UKRI is primarily funded through the Science Budget by the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS).
For this reason, funded projects must reflect the national research priorities agreed in consultation with Government and other stakeholders.
UKRI comprises nine organisations and include seven Research Councils, Innovate UK and Research England (mainly for university funding). UKRI also has its own funding streams:
Other UK government departments
A number of Government departments provide significant funding for a wide variety of research activities. The Department of Health (DH) funds significant programmes of research and development in the NHS through the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), ad-hoc and arm’s length research budgets (allocated for example to Public Health England).
The NIHR has compiled a list of non-commercial partners who manage automatically eligible funding streams, and can be downloaded from their website.
Charities
Charities provide an independent research funding stream that complements the objectives of the Research Councils and Government departments. Charity Funding can range from small pump-priming grants to substantial funds intended for research programmes.
Due to the way charities generate income (donations, legacies and charity shops) they are required to adhere to certain obligations and restrictions on how they use their charitable funds. For instance, charities can only fund non-commercial research that falls within their charitable objectives, particular disease or condition, or more widely benefits health through education and research.
Association of Medical Research Charities (AMRC)
The AMRC is a membership organisation of the leading UK charities that fund medical and health research. There AMRC consists of over 150 member charities, including the world’s largest charity, the Wellcome Trust.
National academies
The UK’s four National Academies support researchers (industry and policy makers) from a broad range of disciplines in academia, industry, charities, and the public sector by providing:
- independent fellowships of world-leading scholars and researcher
- a funding body that supports new research, nationally and internationally
- advocacy for their respective research fields
- a forum for debate and engagement
To find out more about the individual academies visit
- Royal Society (postdoctoral grants)
- The British Academy (humanities and social sciences grants)
- The Royal Academy of Engineering (engineering grants)
- The Academy of Medical Sciences (biomedical and health research grants and more)
European commission
The UK Research Office (UKRO) is the UK's leading national information and advice service on European Commission funding for research and higher education, and their mission is to promote effective UK participation in European Commission funded research programmes, higher education programmes, and other related activities.
Information on funding opportunities, application process and details of support is available at UK Research Office (UKRO).
Internal schemes
Commercial funding
A wide range of research activities are funded by industry and the private sector. When entering into negotiation with industry, a good understanding of the market context is critical.
The Research Operations Team has contract negotiators who can liaise with companies on behalf of researchers to work out the terms and conditions of funding, including publication and ownership of arising Intellectual Property.
National Institute for Health Research (NIHR)
The National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) is England’s largest funder of health and care research.
Working in partnership with the NHS, universities, local government, other research funders, patients and the public, they fund, enable and deliver world-leading health and social care research that improves people's health and wellbeing and promotes economic growth.
The NIHR Health Research Systems depicts the various ways in which the NIHR drives research excellence:
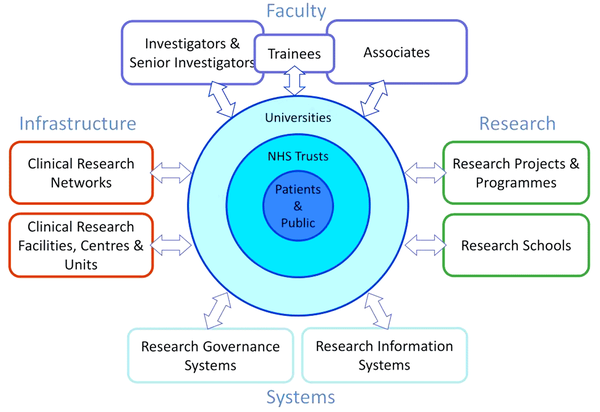
- Infrastructure:
- Investing in world-class infrastructure and a skilled delivery workforce to translate discoveries into improved treatments and services
- Partnering with other public funders, charities and Industry to maximise the value of research to patients and the economy
- Faculty:
- Attracting, training and supporting the best researchers to tackle the complex health and care challenges of the future.
- Research:
- Funding, supporting and delivering high quality research that benefits the NHS, public health and social care
- Engaging and involving patients, carers and the public in order to improve the reach, quality and impact of research
A wide range of NIHR training and career development are provided via the NIHR learning hub, such as 'Working in and with the CRN' and 'Next Steps in delivering clinical research’.
To find out more about studies supported by the National Institute for Health Research Clinical Research Network (NIHR CRN), navigate to the NIHR CRN Portfolio search tool.
NIHR support for nurses, midwives and allied health professionals (NMAHPs)
The National Institute for Health Research has a mission to “provide a health research system in which the NHS supports outstanding individuals working in world class facilities, conducting leading edge research focused on the needs of patients and the public”.
Clinical research nurses, midwives and allied health professionals (NMAHPs) play an important role in the delivery of high quality research care. The NIHR Academy together with the Imperial College Academic Health Science Centre (AHSC) support the development of NMAHPs by raising awareness of their roles through a number of campaigns and initiatives, and providing:
- career support and training
- leadership development opportunities (eg NIHR 70@70 Research Leadership programme)
- networking events
- mentoring opportunities
- guidance on research funding
To find out more about the NMAHPs opportunities:
NIHR Academy
E: academy@nihr.ac.uk
T: 0113 532 8444
W: NIHR Academy
Imperial College Academic Health Science Centre (AHSC)
Clinical Academic Training Office
E: cato@imperial.ac.uk
T: 020 3313 7397
W: Clinical Academic Training Office/NMAHPPs
Setting up a project
The research process follows a series of steps that are governed by set local and national standards.
Our resource guide will help you, aspiring researcher, make sense of the process, and understand what preparations and arrangements need to be considered when setting-up a study at Chelsea and Westminster Hospital NHS Foundation Trust.
The regulatory and governance approvals you need to apply for, for instance sponsorship, HRA and Ethics approval, will vary depending on the type of study, participants involved and research sites.
Is your proposal research, a service evaluation or audit?
- Difference between audit, research and service improvement
- Guidance on investigative projects: Is my project research, a service evaluation or an audit?
The Health Research Authority (HRA) has published a Decision Making Toolkit to help you determine whether your project is classified as research under the definition of the UK Department of Health and Social Care.
Please contact the Research Operations Team if you are unsure about the nature of your project.
Who is your sponsor (e.g. Trust, University or NIHR) and responsible for all project affairs?
- Research Finances
- Indemnity
- Protocol Management
- Information sheets/consent forms
- Compliance i.e. with General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Human Tissue Act, etc.
Did you seek all the relevant regulatory and/or ethics approvals?
- Health Research Authority
- The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA)
- Health and Social Care Research Ethics Committee (HSC REC)
Research process

1. Research idea to sponsorship
- Establish that the idea is research
- Develop the idea—write protocol
- Establish how the research will be funded
- Write the rest of the study documents (eg patient information, informed consent form)
- Obtain a sponsor (for Chelwest sponsorship contact R&D on chelwest.research@nhs.net)
- Get your research proposal peer reviewed (2 peer review forms needed for portfolio adopted studies)
- Complete the sponsorship form
- Send the draft IRAS form, study documents, peer review form(s), sponsorship form, confirmation of funding arrangements and GCP certificate to R&D
- Once R&D have confirmed sponsorship (ie returned the sponsorship form with the ‘for office use only’ section completed by the R&D reviewer) you can submit IRAS application with study documents signed off by chief investigator
2. Feasibility
- Obtain regulatory approvals
- Request feasibility assessments from the R&D Team(s) of participating sites through their R&D department
- Feasible studies will progress to the set-up stage and the R&D team will work towards arranging capacity and capability.
3. Site set-up
- Site selection—participating site(s) receive the local information pack for the study
- Capacity and capability
- Issued by R&D once all study documents have been verified, including regulatory approvals, sign-offs from divisional and support services and delegation compliance of staff documents.
4. Start recruitment
- Await green light from sponsor
- Issued once capacity and capability has been confirmed by the R&D Team of the participating site
- Start recruitment (researcher and delivery team)
Health Research Authority (HRA)
The Health Research Authority is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health that provides a unified national system for the governance of health research in the NHS.
HRA Approval is a requirement for research in NHS settings across England. It comprises an assessment of study compliance with applicable regulations and standards and includes a review by an NHS research ethics committee. It allows participating organisations to focus their resources on assessing, arranging and confirming their capacity and capability to deliver the study within their organisation.
An overview of the HRA application process is pictured below:
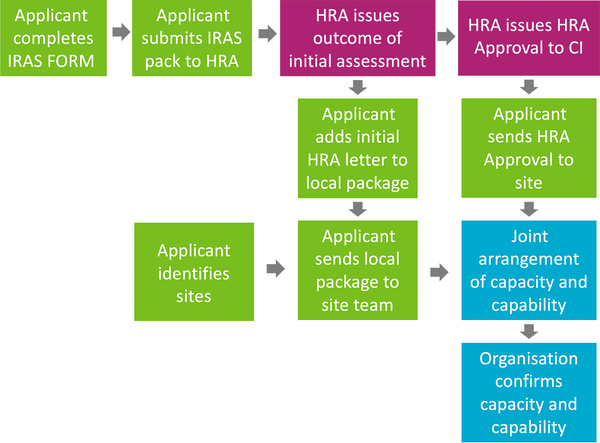
Studies that do not require HRA approval include:
- Research using samples provided by a Tissue Bank
- Research using data provided by a Database with generic ethical approval
- Research taking place in non-NHS setting (e.g. with healthy volunteers)
However, some studies that do not require HRA approval may still need approval from a Research Ethics Committee.
Refer to the HRA Decision Tool to check what approvals you might need, including REC approval.
To learn more about study set-up and HRA approvals, visit the HRA’s eLearning hub via their Learning Management System (LMS).
Sponsorship
All research carried out within the NHS, social care or community care will require a research sponsor. The Sponsor is responsible for ensuring that:
- arrangements are in place for the research team to access resources and support to deliver the research as proposed
- agreements are in place which specify responsibilities for the management and monitoring of the research
For projects that involve the NHS and fall under the UK Policy Framework for Health and Social Care Research Chelsea and Westminster NHS Foundation Trust can act as a Sponsor for its researchers. These projects receive their Health Research Authority (HRA) ethical approval from a dedicated NHS Research Ethics Committee following local sponsorship acceptance by the Trust.
New requests for Trust sponsorship are submitted electronically to the Research Operations Team at chelwest.research@nhs.net.
Sponsorship criteria
The main criteria for sponsorship at Chelsea and Westminster Hospital NHS Foundation Trust include:
- The Chief Investigator (CI) must hold a substantive or honorary contract of employment with the Trust
- Study funding comes through Chelsea and Westminster Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
Documents developed in the process of a sponsorship application
- Applicant’s CV
- Draft Research plan, including study documents: Draft Protocol, Draft Patient/Participant Information Sheets (PIS), Consent Forms (PCF), GP letters, Invitation letters, etc.
- Draft IRAS/Ethics form, or a Combined Review form for CTIMPs
- Details of nominated, independent expert peer reviewers
- Costing breakdown: Draft SoECAT (for all non-commercial studies to be based within the NHS); Authorised costing proposal
- Details of study level funding: Total amount requested (Proposals with potential to attract further external funding (e.g. NIHR funding) must comply with relevant external funding criteria)
Application support
To access templates, Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) and support with your sponsorship and regulatory approvals, contact the Research Operations Team.
Glossary of research roles
- Chief investigator (CI): The person with overall responsibility design, conduct and reporting of a study.
- Principle Investigator (PI): The person delegated responsible for the leadership and conduct of a research study at one site
- Research Delivery Team: Members of the research team who support and/or undertake research-related activities as delegated by the CI and/or PI. DTs may include research nurses, midwives and clinical trials assistants.
- Sponsor: The organisation taking the lead in assuring the study (insurance, compliance, finance etc).
- Funder: The organisation providing the money and/or equipment and/or resources to undertake the project. This could be a trust, a commercial company, a charity or a research councils.
Education and training
We are committed to supporting the on-going professional development of professionals, patients and the public.
Free courses for aspiring researchers:
- Good Clinical Practice (GCP) is an online and face-to-face course made available for free to UK-based researcher by the NIHR. GCP is a set of internationally recognised ethical and scientific quality requirements that must be followed when designing, conducting, recording and reporting clinical research. GCP training is the foundation of any research activity involving human subjects.
- What is Health Research is a free three-week online course co-designed by the NIHR and University of Leeds exploring the world of health research and the role volunteers play in transforming treatments and improving health care.
- Improving Healthcare through Clinical Research is the NIHR's free four-week online course designed for anyone who wants to know more about modern healthcare and the role of clinical research within it.
- Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) covers how treatments and cures are discovered; the impact of clinical research; how we undertake clinical research and why we do clinical research.
To access and book NIHR courses, you will need to register with learn.nihr.ac.uk first using a work based email address. If you have an NIHR Hub/email account you can log in using this. For help contact academy@nihr.ac.uk or view the Get started with NIHR Learn guide.
You can visit the Medical Research Council (MRC) and Health Research Authority (HRA) for further resources.
All those considering research with human subjects at Chelsea and Westminster Hospital NHS Foundation trust must attend a recognised Good Clinical Practice (GCP) training course before starting any research activity.
Tissue bank
The Human Tissue Authority Research License that covers Imperial College Healthcare Tissue Bank (ICHTB) has been extended to include Chelsea and Westminster Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. We are in the process of setting up a satellite tissue bank at St Stephen’s Centre.
This will enable researchers at Chelsea and Westminster Hospital to collect, store and use human tissue appropriately whilst complying with legislation and regulation.
If you want to start collecting samples for specific projects or if you want to transfer left over diagnostic materials to ChelWest’s Tissue Bank, please contact chelwest.tissuebank@nhs.net.

