Eustachian tube dysfunction
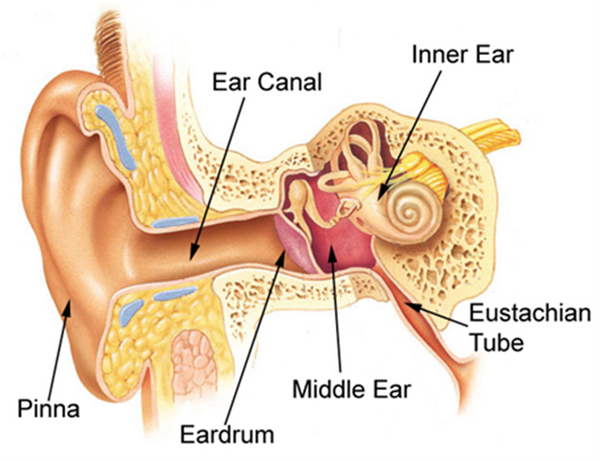
What is eustachian tube dysfunction?
The prolonged failure to equalise pressure in the middle ear. This inadequate ventilation of the chamber behind the eardrum can be the result of sinus, throat, nose and ear conditions, including common colds and allergies.
What are the symptoms?
The main symptom is muffled or dull hearing, often described as being underwater or ears with cotton wool.
Ear pain can be due to a pressure difference causing the drum to over stretch. Other symptoms include fullness in the ear (pressure), tinnitus (ringing), dizziness, popping or clicking noises.
Treatment
If the symptoms are mild usually it will resolve on its own.
Yawn or open your mouth widely as if you were yawning. Eating and drinking may also mobilise the Eustachian tube to allow some air travel through the tube.
Valsalva and Toynbee manoeuvres can be done to push some air into middle ear, take a deep breath, pinch your nose and close your mouth, and gently pop your ears. Do not be very forceful. Some balloons and auto-inflation devices are designed to direct air to the middle ear and promote emptying of middle ear fluid and are available over the counter or online.
Nasal decongestants may be used if there is some blockage. This is available over the counter. GP may prescribe steroid nasal sprays for persistent inflammation.
Steam inhalations with menthol, eucalyptus, or other oils in boiling water in the sink with a towel over the head or any other kind of inhalation device.
Sucking a boiled sweet such as menthol or eucalyptus to unblock the nose.
Taking antihistamines if the swelling is caused by allergies.
If the symptoms persists for over 3 weeks it is advised to see a specialist to investigate it further.

